With the rise of diverse, distributed, and complex environments, agility in data management is a mission-critical priority for data-driven organisations.

Data and analytics leaders have now begun to look beyond traditional data management practices, shifting towards modern solutions like AI-enabled data integration to reduce human errors and overall costs.
To help solve the rising demand for such real-time and event-driven data sharing, the emerging design concept called “data fabric” can be a robust solution. It tackles the data management challenges such as high-cost and low-value data integration cycles.
What is Data Fabric?
Data fabric is an integrated layer (fabric) design concept that serves as a structure for data and connecting processes. The data fabric utilises continuous real-time analytics over the existing metadata assets to support the design, deployment and utilisation of integrated and reusable data across all environments, including hybrid and multi-cloud platforms. Such a structure leverages both human and machine capabilities to access data in place or support where appropriate. A member of an organisation anywhere in the world can access the data and its changes in real-time, enabling frictionless access and data sharing in a distributed data environment.
Why Is It Relevant?
As the traditional data integration no longer meets new business demands of real-time connectivity, data-centric organisations are now faced with the growing need for an approach that overcomes the hurdles of time, space, different software types, and data locations.
Everyone is connected to the internet, and every platform has become a source of data. Maximising the value of data present has become a complex problem. If organisations want to productise or operationalise their AI and ML, they need data to be collected, transformed, and processed. Data fabric can help overcome such problems, providing an all-in-one solution. Data fabric, when implemented, can collect and process data from underlying systems to supply data products on-demand, for either offline or online use cases.
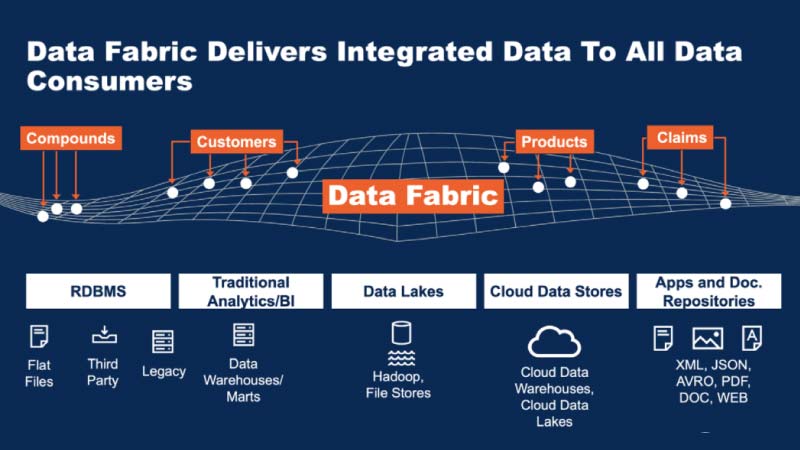
It continuously identifies and connects data from unalike applications to help discover unique and business-relevant relationships between the available data points. This insight supports re-engineered decision-making, providing more value through rapid access and comprehension than traditional data management practices.
For instance, a supply chain manager using a data fabric can add the newly encountered data assets to known relationships between the supplier delays and production delays more rapidly and improve decisions with the new data for new suppliers or customers.
Data fabric capabilities are relevant to all kinds of organisations running multi-cloud and hybrid environments as it offers a range of business value propositions by addressing the technical challenges of operating data services.
How It Works
Data fabric begins with online transaction processing (OLTP). During the online transactional processing, detailed information about every transaction is inserted, updated, and uploaded to the database. The data is then structured, cleaned, and stored in silos at a centre for further usage. At any point in the fabric, any user of the data can take the raw data and use it in a unique way to derive multiple findings, helping organisations leverage their data to grow, adapt, and improve.
Data fabric can help prepare factual data to meet the needs of AI and ML automatically and at sustainable levels. Machine learning can proactively provide the data and insights, helping decision-makers gain better insights and information in a timely manner. The most desirable outcome lies in discovering hidden insights from data, without explicitly looking for, while finding solutions for problems or articulating business insights.
The massive amounts of data that businesses can access need to be exploited to derive unique insights. Areas including forecasting, sales and supply chain optimisation, marketing, and consumer behaviour give the organisation a competitive edge and data leadership. Real-time insight derivation can make an organisation a cut above the rest, and futuristic concepts such as data fabric, are coming to the rescue.
If you liked reading this, you might like our other stories
Company Close-Up: Denodo — Delivering Value From Data
5 Ways to Harness the Power of Website Personalisation









